In the previous three posts I described some custom LAMBDA() functions which perform actions that can be useful for data analysis: creating a CROSS JOIN product (CrossJoin()), returning the relative position of data points which match a particular search criteria (FindItem()), and unpivoting a table of data to flat-file-style vertical data table (UnPivot).
As such I opted to combine these three functions into a single function module which can be imported to and accessed via the Excel Labs Advanced Formula Environment (AFE).
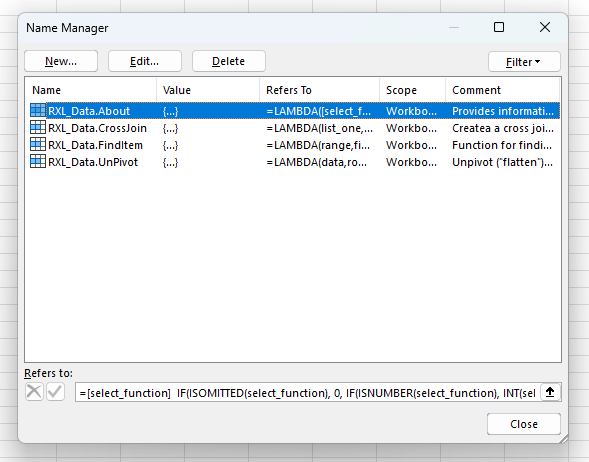
Data Analysis Tools Module (RXL_Data)
Below is the final, combined LAMBDA() module which incorporates an About() function, along with the CrossJoin(), FindItem(), and UnPivot() functions.
The functions are shown in outline only, concentrating instead on the format and structure of the comments, documentation, and definitions. Details on the contents of the module functions can be found in the individual posts for the main three functions (Data Analysis Tools (1) – CrossJoin Lists, Data Analysis Tools (2) – UnPivot Data, Data Analysis Tools (3) – FindItem Function), and details of the About() function can be found in the previous Workbook Information Functions (Part 2).
/*
MODULE: RXL_Data
AUTHOR: R Silk, RXL Development
WEBSITE: https://excel-bits.net
GIST URL: https://gist.github.com/r-silk/e66b3b83363166862c83a5246dc1d3ea
VERSION: 1.03 (May-2025)
*/
/*
Name: About()
Version: 1.10 (23-Apr-2025) -- R Silk, RXL Development
Description: *//**Provides information about the functions in this module*//*
Parameters:
+ select_function = (optional) the name or index number of the function that user wants information about
Error codes:
#[Error: name not recognised] = the provided name string does not match those in the module
#[Error: index not recognised] = the provided index number does not match those in the module
Notes:
- if the select_function input is omitted or an index of 0 is provided then a table of information about the module is returned
- the user can either provide the index of the chosen function as an integer (1+), or the name of the chosen function as a string
*/
About = LAMBDA(
...
);
/*
Name: CrossJoin()
Version: 1.06 (12-Apr-2025) -- R Silk, RXL Development
Description: *//**Createa a cross join (Cartesian join) between two lists; each row of 2nd list is joined to each row of 1st list*//*
The provided input lists can be 1D or 2D arrays, and can be vertically or horizontally oriented
Where a 2D input array is provided the function can optionally convert this to 1D array/list prior to joining the input lists
Parameters:
+ list_one = (required) The 1st input array/list to which the 2nd input array will be joined; should be a valid cell reference
+ list_two = (required) The 2nd input array/list which is joined to the 1st input array/list; should be a valid cell reference
+ convert_list_one = (optional) A True/False value which determines whether to convert list_one to a 1D list / a single column list before the join
Will default to FALSE (0) if not supplied
+ list_one_by_column = (optional) A True/False value -- if list_one is to be converted to a 1D list, this input determines whether to read list_one by column (TRUE) or by row (FALSE)
Will default to TRUE (1) if not supplied
+ convert_list_two = (optional) A True/False value which determines whether to convert list_two to a 1D list / a single column list before the join
Will default to FALSE (0) if not supplied
+ list_two_by_column = (optional) A True/False value -- if list_two is to be converted to a 1D list, this input determines whether to read list_two by column (TRUE) or by row (FALSE)
Will default to TRUE (1) if not supplied
+ replace_blanks = (optional) A value (number or string) which is used to replace any blank cell values in list_one and list_two before the join
+ filter_blanks = (optional) A True/False value which determines whether to filter out blank rows in list_one and/or list_two before the join
Will default to FALSE (0) if not supplied
+ filter_errors = (optional) A True/False value which determines whether to filter out rows in list_one and/or list_two which contain error values -- filtering occurs before the join
Will default to FALSE (0) if not supplied
+ distinct_rows = (optional) A True/False value which determines whether to keep only distinct/unique rows within the output array (TRUE) or provide all calculated rows (FALSE) -- assessed after the join
Will default to FALSE (0) if not supplied
+ vertical_output = (optional) A True/Fasle value which determines whether to provide the calculated output array in a vertical (TRUE) or horizontal (FALSE) orientation
Will default to TRUE (1) if not supplied
Error codes:
#REF! = Occurs where either the list_one or list_two inputs are not valid references
#VALUE! = Occurs when one of the optional inputs (other than the replace_blanks input) is not a valid input, i.e. a number of a logical/Boolean value
Notes:
- The input arrays/lists (list_one, list_two) can be provided as either 1D (single row or single column) or 2D arrays (multiple rows and columns).
-- the function will evaluate whether the input lists should be considered vertical (more rows than columns) or horiztonal (more columns than rows) and transpose as appropriate so that both lists are vertical before the join.
-- this functionality defaults to an assumed vertical orientation if the input list has an equal number of rows and columns
- If a 2D input array is provided for either list_one or list_two, this can be converted to a 1D array (single column) before the join.
- Using the filter_blanks parameter, input rows where all cells are blank values can be filtered out; if at least one value on the row is not blank then the row is not filtered out.
- As the replacement of any blank values (using any supplied replace_blanks input) is processed prior to filtering steps, if the replace_blanks input is used then the filter_blanks parameter will have no effect.
- Using the filter_errors parameter, input rows where at least one cell value is an error code, then the row is filtered out.
*/
CrossJoin = LAMBDA(
...
);
/*
Name: FindItem()
Version: 1.08 (27-Apr-2025) -- R Silk, RXL Development
Description: *//**Function for finding matching values within a source array*//*
For each match that is found, the function can return the matched values, relative position of the match within the source array or worksheet, or the cell Address.
Match logic can be chosen beyond simply equal-to-matching logic, including a partial text match and regular exoression (RegEx) test.
Parameters:
+ range = (required) Range of cells containing the source array to look within; can be a 1D or 2D array in any ortientation.
+ find_item = (required) The value to look for within the source range.
This can be a number, a text string, or a cell reference, but should be a single value rather than an array.
If the RegEx match_type option is selected, the find_item value is used as the regular expression string.
+ match_type = (optional) Single value (can be a number or text string) to determine the match type to use to find values.
Valid inputs are a number between 0 and 6, or a valid string from the list below; If not supplied, will default to 0.
"=" 0 = (default) uses euqal-to matching logic
"<>" 1 = uses not-equal-to matching logic
">" 2 = uses greater-than matching logic
"<" 3 = uses less-than matching logic
">=" 4 = uses greater-than-or-equal-to matching logic
"<=" 5 = uses less-than-or-equal-to matching logic
"find" 6 = attempts to find a sub-string / part-string within the source values; uses non-case sensitive search
"regex" 7 = uses a regular expression (RegEx) to test the source values and match if TRUE
+ output_type = (optional) Single number between 0 and 5 to determine the function output type/format; if no value is provided, will default to 0.
0 = (default) list of matched values in vertical orientation
1 = the relative position of each match within the source array, in the format: [row],[col]
2 = the absolute position of each match within the source worksheet, in the format: [row],[col]
3 = the cell address of each match using the cell reference format: A1
4 = the absolute cell address of each match using the cell reference format: $A$1
5 = the count of the number of found matches
+ if_not_found = (optional) Single value (can be a number or text string) which is returned by the function if no matches are found.
If not supplied, the function will default to returning a #N/A value.
+ add_header = (optional) A True/False value to determine whether or not to add a header row to the function output array.
The input can be either TRUE/FALSE or 1/0.
If not supplied, will default to FALSE (0).
+ split_output = (optional) A True/False value to determine whether or not split the output array into two columns as appropriate.
If the output_type selected is relative or abolsute position, then this option can split the position of each match into a 2 column array for row and column values.
The input can be either TRUE/FALSE or 1/0.
If not supplied, will default to FALSE (0).
Error codes:
#REF! = Invalid cell reference provided for the range input, or a broken cell reference within any of the inputs
#VALUE! = match_type parameter is invalid -- not a number between 0 and 6 or one of the expected/allowed input strings
#VALUE! = output_type parameter is invalid -- not a number between 0 and 5
Notes:
- The partial text match is non-case sensitive; for a case sensitive partial text match, use the RegEx test matching logic with a sub-string to find rather than a regular expression string.
*/
FindItem = LAMBDA(
...
);
/* RXL_UnPivot Function
version 1.07 (07-May-2025)
R Silk, RXL Development
https://gist.github.com/r-silk/c31faf1e9de8d01687447bede455f8cc
*/
/*
Name: UnPivot()
Description: *//**Unpivot ("flatten") a 2D source array into a vertical data table; each source data point represented as an individual row*//*
The main data points are held within a Values column, and the row titles/headers and column headers from the source data table are used to add details as Key and Name columns
Parameters:
+ data = (required) An array containing the main data points from the table to unpivot or "flat-file".
+ row_headers = (required) An array of values which represent the row headers/titles for the main data input array.
The row_headers input array should have the same number of rows as the data input array; there can be one or more columns in the row_headers input array.
+ column_headers = (required) An array of values which represent the column headers/titles for the main data input array.
The column_headers input array should have the same number of columns as the data input array; there can be one or more rows in the column_headers input array.
+ by_column = (optional) A True/False input which determines whether the main data input array should be read by column (TRUE), or by row (FALSE).
TRUE = the data array is read by going down each column (top-to-bottom), using the column_headers as the Key column(s) and the row_headers as the Name column(s)
FALSE = the data array is read by going across each row (left-to-right), using the row_headers as the Key column(s) and the column_headers as the Name column(s)
If not supplied, will default to FALSE (therefore reading the data array by row).
+ replace_data_blanks = (optional) A value which can be used to replace any blank data points in the Value column, as per the main data input array.
If the input provided is a number or text string, then this value is used to replace any blank data points.
If the input provided is a logical/Boolean value:
TRUE = blank data points will be replaced with a #N/A error value
FALSE = blank data points will not be replaced
If not supplied, will default to an effective blank string value ( "" ).
+ filter_blanks = (optional) A True/False input which determines whether to filter out any rows with blank data points within the Values column.
Can be input as TRUE/FALSE (Boolean logical value) or 1/0 (number).
If not supplied, will default to FALSE.
+ filter_errors = (optional) A True/False input which determines whether to filter out any rows with error values within the data values column.
Can be input as TRUE/FALSE (Boolean logical value) or 1/0 (number).
If not supplied, will default to FALSE.
+ fill_row_blanks = (optional) Determines whether any blank data points in the row_headers input array should be filled and what value should be used.
The blank cells can be filled with the values from the cells above or below the blank cell, or with a specified value.
+1 = fills the blank data point with the cell value from the row above
-1 = fills the blank data point with the cell value from the row below
0 = does not fill the blank values from the input array, instead they are left as an empty string ( "" ) in the output
TRUE = fills the blank data points with the cell value from the row above
FALSE = does not fill the blank values from the input array, instead they are left as an empty string ( "" ) in the output
[text] = any value other than a number or TRUE/FALSE is provided this is used to fill all blank values
If not supplied, will default to FALSE/0
+ fill_column_blanks = (optional) Determines whether any blank data points in the column_headers input array should be filled and what value should be used.
The blank cells can be filled with the values from the cells to the Left or Right of the blank cell, or with a specified value.
+1 = fills the blank data point with the cell value from the cell to the Left
-1 = fills the blank data point with the cell value from the cell to the Right
0 = does not fill the blank values from the input array, instead they are left as an empty string ( "" ) in the output
TRUE = fills the blank data points with the cell value from the cell to the Left
FALSE = does not fill the blank values from the input array, instead they are left as an empty string ( "" ) in the output
[text] = any value other than a number or TRUE/FALSE is provided this is used to fill all blank values
If not supplied, will default to FALSE/0
+ output_vertical = (optional) A True/False input which determines whether to provide the final output data array in vertical orientation or horizontal orientation.
Can be input as TRUE/FALSE (Boolean logical value) or 1/0 (number).
TRUE = vertical orientation
FALSE = horizontal orientation, running left-to-right across the worksheet
If not supplied, will default to FALSE.
Error codes:
#VALUE! = Occurs when one or more of the inputs provided are invalid.
#CALC! = Occurs where the data array dimensions are not the equal to the corresponding dimenesions of the row and column header input arrays.
i.e. the row headers array and data array should have the same number of rows
the column headers array and data array should have the same number of columns
Notes:
- The replace_data_blanks, filter_blanks, and filter_errors functionality does not consider any blank or error values within the Key column(s) or Name column(s), only the Values column (data array).
- Additionaly, if the replace_data_blanks option is used, then the filter_blanks option will have no effect on the output as the blank values are replaced before any filtering occurs.
- If the replace_data_blanks option is used to replace blank data values with #N/A values, then these could then be filtered out by the filter_errors option as the filtering occurs after dealing with blank data points.
*/
UnPivot = LAMBDA(
...
);
The above shows my current preferred format for these Excel Labs AFE modules, making use of multi-line comments to provide the module and function documentation. Using comments in this way for the function documentation allows for more extensive and more verbose information but is only accessible via the Excel Labs add-in. Therefore, I also like to add in the About() function to provide more easily accessible function information on the worksheet.
The initial comment block (lines 1-7) provides the information on the module itself including the suggested module name and version number. I then include the About() function (lines 8-26) followed by the other functions in the order in which I have included them in the About() function information strings.
Each function is declared and defined in the standard Excel Labs AFE way, starting with the function name and ending with a semi-colon:
Function_Name = LAMBDA( ... );
Above each function declaration, I use a multi-line comment block to supply the corresponding function documentation (for example see lines 28-65). This will usually contain:
- function name;
- function version;
- description of the functions action/intended use;
- input parameters, including information on:
- whether a parameter is required or optional, and
- the expected input value(s);
- potential function output error codes and there meaning; and
- any additional notes on how the function is intended to work.
Of note, the description portion of the function documentation is held in its own separate and special comment block. This comment block uses a double asterisk in the format:
/** [Description text] */
This is important, as the double asterisk comment format indicates to the AFE that this text should be used to populate the Comment property of the defined name that stores the function. As described above the Comment property of the defined function is then displayed to the user when selecting a function to use in their formulae.
Note: The description supplied in the double asterisk comment (“/** … */”) should be a brief description over a single line as there is a 255 character limit for the text stored in the defined name Comment property.

If you wish to use the RXL_Data module (or any other AFE module) in your Excel projects, this can be easily achieved using the below steps:
- Ensure that you have the Microsoft Excel Labs add-in installed, and navigate to the Advanced Formula Environment (AFE) tab
- In the AFE choose the Modules section from the green ribbon at the top
- Click on the “Import from URL” button in the black ribbon (looks like a cloud with a down arrow)

- In the dialogue box that pops up enter the GitHub Gist URL for the
RXL_Datamodule (https://gist.github.com/r-silk/e66b3b83363166862c83a5246dc1d3ea) - Before clicking the “Import” button, check the box for “Add formulas to a new module?” and add the suggested module name to the text box that appears.

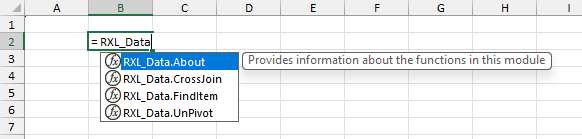
Once the module has been uploaded, the AFE will save a copy of the full module string complete with code comments in your Excel file, which can then be read via the Excel Labs add-in. The AFE will also save copies of each defined function in the Name Manager as defined names with the specified Comments property, and so you can start using the functions by simply typing =RXL_Data in the formula bar.

Leave a comment